EIGRPのサクセサとフィージブルサクセサを確認する <1>
EIGRP には、サクセサとフィージブルサクセサがあります。
ルートの選択はメトリックで決まりますので、サクセサにはメトリック値が一番小さいルートが選択されます。
そしてこのサクセサがダウンした時に、すぐに別のルートを用意できるようにフィージブルサクセサが事前に選ばれています。
宛先ネットワークまでのパスがあれば、どんなルートでもフィージブルサクセサになれるというわけではありません。フィージブルサクセサになるためには以下の条件を満たさなくてはいけません。
例えば、次のようなネットワーク構成を考えてみましょう。
RT-A から PC-C のあるネットワーク 172.16.0.0/16 に到達するためのサクセサとフィージブルサクセサを求めていきます。

RT-A からネットワーク 172.16.0.0/16 に行くには、次の2つのルート(A と B のルート)があります。

RIP のメトリックはホップ数 (通過するルータの数) で決まるので、回線速度 (どのルートを通ったら速いか?) には関係ありませんが、EIGRP では帯域幅がメトリックに入っているので、最も速く宛先ネットワークに到達するルート (帯域幅が広いルート) が最適ルートとして選ばれます。
384Kbps の回線を1つ通るのと、
384Kbps の回線と 512Kbps の回線の2つを通るのでは、
384Kbps の回線を1つ通る方が速いに決まっていますので、A ルートが最適ルート (サクセサ) に選ばれます。
あとは、B ルートがフィージブルサクセサに選ばれるかどうかですが、これは
では計算してみましょう。
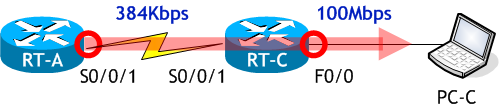
まず、A ルートを計算します。
帯域幅と遅延はインターフェイスの種類によって決まっています。
ただし、回線速度と同じ帯域幅をシリアルインターフェイスに設定することにより以下のようになります。
A ルートでの最少帯域幅は「BW 384 Kbit」です。
遅延は両方の遅延「DLY 20000 usec」と「DLY 100 usec」の合計です。
次は B ルートを求めます。
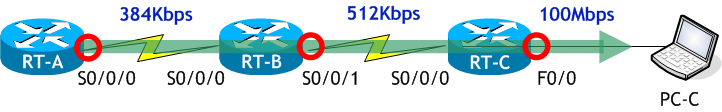
B ルートでの最少帯域幅も「BW 384 Kbit」です。
遅延は「DLY 20000 usec」と「DLY 20000 usec」と「DLY 100 usec」の合計です。
では次に B ルートの AD を求めます。
B ルートの AD は、RT-A にとってのネイバーである RT-B から宛先ネットワーク 172.16.0.0/16 までのメトリックです。
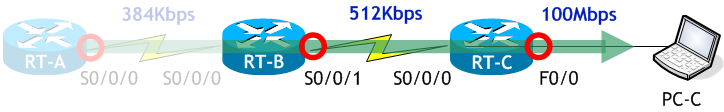
最少帯域幅は「BW 512 Kbit」です。
遅延は両方の遅延「DLY 20000 usec」と「DLY 100 usec」の合計です。
| サクセサ | 最適ルート | ルーティングテーブルとトポロジーテーブルに載る |
|---|---|---|
| フィージブルサクセサ | 代替ルート | トポロジーテーブルに載る |
そしてこのサクセサがダウンした時に、すぐに別のルートを用意できるようにフィージブルサクセサが事前に選ばれています。
サクセサがダウン → フィージブルサクセサがサクセサに昇格
そして、フィージブルサクセサがサクセサに昇格した時点で、パケットの転送用ルートとして使われます。宛先ネットワークまでのパスがあれば、どんなルートでもフィージブルサクセサになれるというわけではありません。フィージブルサクセサになるためには以下の条件を満たさなくてはいけません。
サクセサの FD > フィージブルサクセサの候補となるルートの AD
この条件を満たさなければ、フィージブルサクセサにはなれず、メトリック値が大きくてもこの条件を満たすルートがフィージブルサクセサとして選ばれます。
例えば、次のようなネットワーク構成を考えてみましょう。
RT-A から PC-C のあるネットワーク 172.16.0.0/16 に到達するためのサクセサとフィージブルサクセサを求めていきます。

RT-A からネットワーク 172.16.0.0/16 に行くには、次の2つのルート(A と B のルート)があります。

RIP のメトリックはホップ数 (通過するルータの数) で決まるので、回線速度 (どのルートを通ったら速いか?) には関係ありませんが、EIGRP では帯域幅がメトリックに入っているので、最も速く宛先ネットワークに到達するルート (帯域幅が広いルート) が最適ルートとして選ばれます。
384Kbps の回線を1つ通るのと、
384Kbps の回線と 512Kbps の回線の2つを通るのでは、
384Kbps の回線を1つ通る方が速いに決まっていますので、A ルートが最適ルート (サクセサ) に選ばれます。
あとは、B ルートがフィージブルサクセサに選ばれるかどうかですが、これは
サクセサ (Aルート) の FD > フィージブルサクセサ候補 (Bルート) の AD
を満足するかどうかで決定します。では計算してみましょう。
まず、A ルートを計算します。

帯域幅と遅延はインターフェイスの種類によって決まっています。
| インターフェイス | 帯域幅 | 遅延 |
|---|---|---|
| FastEthernet | BW 100000 Kbit | DLY 100 usec |
| Serial | BW 1544 Kbit | DLY 20000 usec |
| インターフェイス | 帯域幅 | 遅延 |
|---|---|---|
| FastEthernet | BW 100000 Kbit | DLY 100 usec |
| Serial (384Kbps) | BW 384 Kbit | DLY 20000 usec |
| Serial (512Kbps) | BW 512 Kbit | DLY 20000 usec |
遅延は両方の遅延「DLY 20000 usec」と「DLY 100 usec」の合計です。
帯域幅 = 10^7/384 = 26041
遅延 = (20000+100)/10 = 2010
したがって、A ルートのメトリック (FD) は遅延 = (20000+100)/10 = 2010
メトリック = (26041+2010)×256 = 7181056
となります。
次は B ルートを求めます。

B ルートでの最少帯域幅も「BW 384 Kbit」です。
遅延は「DLY 20000 usec」と「DLY 20000 usec」と「DLY 100 usec」の合計です。
帯域幅 = 10^7/384 = 26041
遅延 = (20000+20000+100)/10 = 4010
したがって、B ルートのメトリック (FD) は遅延 = (20000+20000+100)/10 = 4010
メトリック = (26041+4010)×256 = 7693056
となり、A ルートのメトリックよりも大きな値です。
では次に B ルートの AD を求めます。
B ルートの AD は、RT-A にとってのネイバーである RT-B から宛先ネットワーク 172.16.0.0/16 までのメトリックです。

最少帯域幅は「BW 512 Kbit」です。
遅延は両方の遅延「DLY 20000 usec」と「DLY 100 usec」の合計です。
帯域幅 = 10^7/512 = 19531
遅延 = (20000+100)/10 = 2010
したがって、B ルートの AD は
遅延 = (20000+100)/10 = 2010
AD = (19531+2010)×256 = 5514496
となります。
A ルートの FD (=7181056) > B ルートの AD (=5514496)
この条件は満たされますので、B ルートはフィージブルサクセサになります。
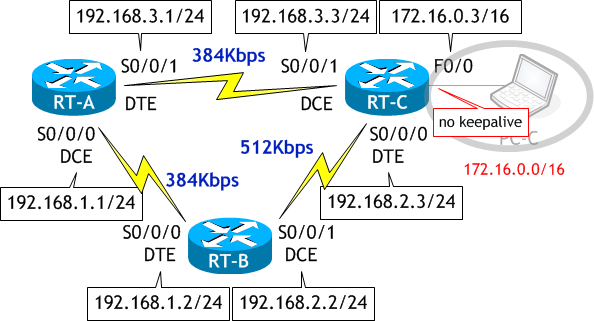
ネットワーク構成図
- RT-A に以下の設定をしなさい。
- RT-B に以下の設定をしなさい。
- RT-C に以下の設定をしなさい。
- RT-A のルーティングテーブル (EIGRP) を表示させなさい。
- RT-A のトポロジーテーブルを表示させなさい。
- RT-B、RT-C のルーティングテーブル (EIGRP) を表示させなさい。
- RT-A、RT-B、RT-C のネイバーテーブルを表示させなさい。
- RT-B、RT-C のトポロジーテーブルを表示させなさい。
- RT-A、RT-B、RT-C で sh ip protocols コマンドを実行しなさい。
| ホスト名 | RT-A |
|---|---|
| S0/0/0 のIPアドレス | 192.168.1.1/24 |
| S0/0/0 のクロックレートと帯域幅 | 384Kbps |
| S0/0/1 のIPアドレス | 192.168.3.1/24 |
| S0/0/1 の帯域幅 | 384Kbps |
| ルーティングプロトコル | EIGRP |
| AS 番号 | 10 |
< RT-A > Router# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# host RT-A RT-A(config)# int s0/0/0 RT-A(config-if)# ip add 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 RT-A(config-if)# clock rate 384000 RT-A(config-if)# bandwidth 384 RT-A(config-if)# no shut RT-A(config-if)# int s0/0/1 RT-A(config-if)# ip add 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 RT-A(config-if)# bandwidth 384 RT-A(config-if)# no shut RT-A(config-if)# router eigrp 10 RT-A(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 RT-A(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 RT-A(config-router)# ^Z RT-A#
| ホスト名 | RT-B |
|---|---|
| S0/0/0 のIPアドレス | 192.168.1.2/24 |
| S0/0/0 の帯域幅 | 384Kbps |
| S0/0/1 のIPアドレス | 192.168.2.2/24 |
| S0/0/1 のクロックレートと帯域幅 | 512Kbps |
| ルーティングプロトコル | EIGRP |
| AS 番号 | 10 |
< RT-B > Router# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# host RT-B RT-B(config)# int s0/0/0 RT-B(config-if)# ip add 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 RT-B(config-if)# bandwidth 384 RT-B(config-if)# no shut RT-B(config-if)# int s0/0/1 RT-B(config-if)# ip add 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 RT-B(config-if)# clock rate 512000 RT-B(config-if)# bandwidth 512 RT-B(config-if)# no shut RT-B(config-if)# router eigrp 10 RT-B(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 RT-B(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0 RT-B(config-router)# ^Z RT-B#
| ホスト名 | RT-C |
|---|---|
| S0/0/0 のIPアドレス | 192.168.2.3/24 |
| S0/0/0 の帯域幅 | 512Kbps |
| S0/0/1 のIPアドレス | 192.168.3.3/24 |
| S0/0/1 のクロックレートと帯域幅 | 384Kbps |
| F0/0 のIPアドレス | 172.16.0.3/16 |
| ルーティングプロトコル | EIGRP |
| AS 番号 | 10 |
< RT-C > Router# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# host RT-C RT-C(config)# int s0/0/0 RT-C(config-if)# ip add 192.168.2.3 255.255.255.0 RT-C(config-if)# bandwidth 512 RT-C(config-if)# no shut RT-C(config-if)# int s0/0/1 RT-C(config-if)# ip add 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.0 RT-C(config-if)# clock rate 384000 RT-C(config-if)# bandwidth 384 RT-C(config-if)# no shut RT-C(config-if)# int f0/0 RT-C(config-if)# ip add 172.16.0.3 255.255.0.0 RT-C(config-if)# no keepalive RT-C(config-if)# no shut RT-C(config-if)# router eigrp 10 RT-C(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0 RT-C(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 RT-C(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 RT-C(config-router)# ^Z RT-C#
< RT-A >
RT-A# sh ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 172.16.0.0/16 [90/7181056] via 192.168.3.3, 00:00:41, Serial0/0/1 ← A ルート
D 192.168.2.0/24 [90/7690496] via 192.168.3.3, 00:00:41, Serial0/0/1
[90/7690496] via 192.168.1.2, 00:00:41, Serial0/0/0
RT-A#
RT-A から 172.16.0.0/16 のネットワークに行くには、A ルートと B ルートがありますが、ルーティングテーブルには最適ルート (サクセサ) である A ルートのみ載ります。
< RT-A >
RT-A# sh ip eigrp topology
EIGRP-IPv4 Topology Table for AS(10)/ID(192.168.3.1)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 192.168.3.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 7178496
via Connected, Serial0/0/1
P 192.168.2.0/24, 2 successors, FD is 7690496
via 192.168.1.2 (7690496/5511936), Serial0/0/0
via 192.168.3.3 (7690496/5511936), Serial0/0/1
P 172.16.0.0/16, 1 successors, FD is 7181056
via 192.168.3.3 (7181056/28160), Serial0/0/1 ← サクセサ (A ルート)
via 192.168.1.2 (7693056/5514496), Serial0/0/0 ← フィージブルサクセサ (B ルート)
P 192.168.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 7178496
via Connected, Serial0/0/0
RT-A#
RT-A から 172.16.0.0/16 のネットワークに行くには、サクセサが1つあり、そのサクセサのメトリック (FD) は 7181056 です。B ルートはフィージブルサクセサです。FD、AD ともに計算値と一致しています。
< RT-B >
RT-B# sh ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 172.16.0.0/16 [90/5514496] via 192.168.2.3, 00:00:51, Serial0/0/1
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/7690496] via 192.168.2.3, 00:00:51, Serial0/0/1
[90/7690496] via 192.168.1.1, 00:00:51, Serial0/0/0
RT-B#
< RT-C >
RT-C# sh ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/7690496] via 192.168.3.1, 00:00:55, Serial0/0/1
[90/7690496] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:55, Serial0/0/0
RT-C#
< RT-A >
RT-A# sh ip eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(10)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
1 192.168.3.3 Se0/0/1 11 00:04:57 5 378 0 7
0 192.168.1.2 Se0/0/0 14 00:05:08 3 378 0 9
RT-A#
< RT-B >
RT-B# sh ip eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(10)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
1 192.168.2.3 Se0/0/1 12 00:05:03 6 282 0 6
0 192.168.1.1 Se0/0/0 11 00:05:14 5 378 0 8
RT-B#
< RT-C >
RT-C# sh ip eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(10)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
1 192.168.2.2 Se0/0/0 14 00:05:16 3 282 0 8
0 192.168.3.1 Se0/0/1 13 00:05:16 4 378 0 7
RT-C#
< RT-B >
RT-B# sh ip eigrp topology
EIGRP-IPv4 Topology Table for AS(10)/ID(192.168.2.2)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 192.168.3.0/24, 2 successors, FD is 7690496
via 192.168.1.1 (7690496/7178496), Serial0/0/0
via 192.168.2.3 (7690496/7178496), Serial0/0/1
P 192.168.2.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 5511936
via Connected, Serial0/0/1
P 172.16.0.0/16, 1 successors, FD is 5514496
via 192.168.2.3 (5514496/28160), Serial0/0/1
P 192.168.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 7178496
via Connected, Serial0/0/0
RT-B#
< RT-C >
RT-C# sh ip eigrp topology
EIGRP-IPv4 Topology Table for AS(10)/ID(192.168.3.3)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 192.168.3.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 7178496
via Connected, Serial0/0/1
P 192.168.2.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 5511936
via Connected, Serial0/0/0
P 172.16.0.0/16, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via Connected, FastEthernet0/0
P 192.168.1.0/24, 2 successors, FD is 7690496
via 192.168.2.2 (7690496/7178496), Serial0/0/0
via 192.168.3.1 (7690496/7178496), Serial0/0/1
RT-C#
< RT-A >
RT-A# sh ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 10"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP-IPv4 Protocol for AS(10)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 192.168.3.1
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.1.0
192.168.3.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.3.3 90 00:06:58
192.168.1.2 90 00:06:58
Distance: internal 90 external 170
RT-A#
< RT-B >
RT-B# sh ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 10"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP-IPv4 Protocol for AS(10)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 192.168.2.2
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.1.0
192.168.2.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.1.1 90 00:07:09
192.168.2.3 90 00:07:09
Distance: internal 90 external 170
RT-B#
< RT-C >
RT-C# sh ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 10"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP-IPv4 Protocol for AS(10)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 192.168.3.3
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
172.16.0.0
192.168.2.0
192.168.3.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.2.2 90 00:07:15
192.168.3.1 90 00:07:15
Distance: internal 90 external 170
RT-C#
※ 次の「シナリオ」に続きます。